Buy a Custom Wealth Chinese or Japanese Calligraphy Wall Scroll
We have many options to create artwork with the Chinese characters / Asian symbols / Japanese Kanji for Wealth on a wall scroll or portrait.
If you want to create a cool Wealth wall scroll, this is the place. Below you will find a few Asian symbols that express the idea of Wealth.
1. Men Die for Wealth, Birds Die for Food
3. Wealth / Fortune / Riches / Abundance
6. Year-In Year-Out Have Abundance
9. Baby
10. The Beatles
11. Beautiful Life / Life in Perfect Harmony
12. Benzaiten
13. Better to be Happy than Rich
15. Cherish
16. Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Chapter 33
17. Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Excerpt
18. Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Chapter 9
19. Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Chapter 54
20. Dark Sister
21. Double Happiness Guest Book
22. The farts of others stink, but one’s own smells sweet
23. A Bright Future
24. Flourish
25. Rise and Fall / Ups and Downs
27. Fu Lu Shou
28. Lucky Star
29. Good Health / Healthy / Vigor
30. Protect Guard Treasure Cherish
31. Guanxi
32. Gung Ho
34. Glory and Honor
35. Hua Mulan
36. I am Enough
37. Three Treasures of Chinese Medicine
38. Mutual Welfare and Benefit
39. Safety and Well-Being of the Family
40. Kindness and Forgiving Nature
41. Contentment
43. Live Together and Help Each Other
44. Large River
46. A Life of Happiness and Prosperity
47. Lioness
48. Just as Liquor Turns a Face Red, Gold Turns a Heart Black
51. Live Free or Die
53. Longevity / Long Life Wishes
54. Love and Protect
55. Energy Sword Body in Concert
57. Precious
59. Prosperity
60. Realize Your Ambitions / Ride on the Crest of Success
62. Prosperity
64. Prosperous Life
65. Red Envelope
67. Siddhartha
68. Star
69. Success
70. Sushi
71. Time is more valuable than Jade
72. Treasure
73. Vinh
74. Wado-Ryu
75. There is one single thread binding my Way together
76. Warrior
77. Washington
78. Worldwide Wish for Peace and Prosperity
80. Boar / Pig
81. Kanazawa-Ryu
83. Seng
84. Luong
Men Die for Wealth, Birds Die for Food
人為財死鳥為食亡 is a Chinese proverb that literally states that human beings will die for riches, just as birds will for food.
Figuratively it means that man will do anything in his means to become rich. Personally, I think dying for food is a more noble cause.
Often translated as “Men die in pursuit of wealth, birds die in pursuit of food. The 人 in this proverb just means human, so “men” is a placeholder for human with that translation - an English language problem that we have no easy gender-neutral nouns.
This proverb is meant to serve as a warning about the follies of greed.
Money / Wealth
金錢/金銭 means money, cash, currency, or wealth in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
Literally, it means “gold coins” but has come to be used to mean money in general, as well as the idea of wealth.
![]() The second character of this word is written in a variant form in Japan. The more common version in Japan is shown to the right. Click on the Kanji to the right instead of the button above if you want this Japanese variant in your calligraphy.
The second character of this word is written in a variant form in Japan. The more common version in Japan is shown to the right. Click on the Kanji to the right instead of the button above if you want this Japanese variant in your calligraphy.
Wealth / Fortune / Riches / Abundance
The title says it all; this word is clearly understood in Chinese and Japanese as well as Korean Hanja.
Wealth / Riches / Fortune
財富 means wealth or riches in Chinese.
Hanging this on your wall will label you as a “lover of money” or a “greedy person.” Order this only if you don't mind being seen in this light.
Five Red Bats
紅五蝠 is a play on words in Chinese because of some homophones.
The first thing you need to know is that the word for bat, 蝠, sounds exactly like the word for good fortune, 福. Thus, bats are often associated with good luck and good fortune in Chinese culture.
Five bats (五福 / 五蝠) means “five fortunes,” referring to luck, prosperity, wealth, happiness, and longevity.
The word red, 红, has the same sound as 宏 meaning vast, great, or magnificent. Therefore, a red bat means “vast fortune.”
Altogether, five red bats represent vast reaches of the five fortunes.
Year-In Year-Out Have Abundance
年年有餘 is a common proverb or wish of prosperity you'll hear around the time of Chinese New Year.
Directly translated character by character, it means “Year Year Have Surplus.” A more natural English translation including the deeper meaning would be “Every Year may you Have Abundance in your life.”
On a side note, this phrase often goes with a gift of something related to fish. This is because the last character, “yu” which means surplus or abundance, has exactly the same pronunciation in Mandarin as the word for “fish.”
This is also one of the most common titles for traditional paintings that feature koi fish.
In China, this phrase might make an odd wall scroll - a customer asked especially for this common phrase which is why it appears here. See my other abundance-related words if you want a wall scroll that will seem more comfortable in Chinese culture.
Note: This can be pronounced in Korean, but it's not a commonly used term.
See Also: Prosperity | Good Fortune
Abundance / Prosperous
富裕 means prosperous, having an abundance, well-to-do, or well-off.
It's a simple word that suggests “you have made it” in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and Korean Hanja.
See Also: Good Fortune
Abundance and Prosperity
繁榮富裕 is a proverb about “Prosperity and Abundance.”
This presents and reinforces the ideas of being prosperous, a booming economy, well-to-do, well-off, wealthy, riches, and opulence.
While this is the ancient/traditional Chinese way to write this, most Japanese can fully read and understand it. It's also the correct form of old Korean Hanja (though few Koreans of the current generation will be able to read this).
See Also: Good Fortune
Baby
寶寶 is how Chinese people express “baby.”
The word is composed of the same character twice, and therefore literally means “double precious” or “double treasure.”
This would be a nice wall scroll to put either inside or by the door of your baby's room (not on the door, as wall scrolls swing around wildly when hung on doors that open and close a lot).
The Beatles
Beautiful Life / Life in Perfect Harmony
和美 is a word that means “harmonious” or, “in perfect harmony.”
The deeper meaning or more natural translation would be something like, “beautiful life.”
The first character means peace and harmony.
The second character means beautiful. But in this case, when combined with the first character, beautiful refers to being satisfied with what you have in your life. This can be having good relations, good feelings, comfort, and having enough (with no feeling of wanting).
Note: In Japanese, this is often used as the name "Wami." This title is probably more appropriate if your audience is Chinese.
Benzaiten
弁財天 is a Buddhist term that can be translated or transliterated as Benzaiten or Saraswati.
弁財天 is the Buddhist goddess of music, eloquence, wealth, and water.
This goddess of eloquence came into Buddhism from the Hindu goddess Saraswati. Benzaiten and Saraswati are considered by most to be one and the same. However, in Japanese culture, Benzaiten has been conflated with several other deities.
Better to be Happy than Rich
安貧樂道 means “It's better to be happy than rich” in Chinese.
Even if you are poor, you should still feel satisfied in your life...
...Satisfaction, happiness and the meaning of your life come from within yourself and not from money or riches of the world.
In Chinese, there are a lot of four-character proverbs which express some very old philosophies.
Though there are only four characters on this scroll, in Chinese, the meanings often surpass the dictionary definition of each character.
In this case, you should not set your expectations too high for the money or riches you wish to have. One who sets their expectations too high is almost always disappointed. Instead, you should cherish what you have, seek to improve yourself from within, and not measure your worth by the size of your bank account.
Blessings on this Home
五福臨門 means “five good fortunes arrive [at the] door.”
It is understood to mean “may the five blessings descend upon this home.”
These blessings are known in ancient China to be: longevity, wealth, health, virtue, and natural death (living to old age). This is one of several auspicious sayings you might hear during the Chinese New Year.
Cherish
Cherish
Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Chapter 33
This is referred to as passage or chapter 33 of the Dao De Jing (often Romanized as “Tao Te Ching”).
These are the words of the philosopher Laozi (Lao Tzu).
To know others is wisdom;
To know oneself is acuity/intelligence.
To conquer others is power,
To conquer oneself is strength.
To know contentment is to have wealth.
To act resolutely is to have purpose.
To stay one's ground is to be enduring.
To die and yet not be forgotten is to be long-lived.
To understand others is to be knowledgeable;
To understand yourself is to be wise.
To conquer others is to have strength;
To conquer yourself is to be strong.
To know when you have enough is to be rich.
To go forward with strength is to have ambition.
To not lose your place is to be long-lasting.
To die but not be forgotten -- that's true long life.
He who is content is rich;
He who acts with persistence has will;
He who does not lose his roots will endure;
He who dies physically but preserves the Dao
will enjoy a long after-life.
Notes:
During our research, the Chinese characters shown here are probably the most accurate to the original text of Laozi. These were taken for the most part from the Mawangdui 1973 and Guodan 1993 manuscripts which pre-date other Daodejing texts by about 1000 years.
Grammar was a little different in Laozi’s time. So you should consider this to be the ancient Chinese version. Some have modernized this passage by adding, removing, or swapping articles and changing the grammar (we felt the oldest and most original version would be more desirable). You may find other versions printed in books or online - sometimes these modern texts are simply used to explain to Chinese people what the original text really means.
This language issue can be compared in English by thinking how the King James (known as the Authorized version in Great Britain) Bible from 1611 was written, and comparing it to modern English. Now imagine that the Daodejing was probably written around 403 BCE (2000 years before the King James Version of the Bible). To a Chinese person, the original Daodejing reads like text that is 3 times more detached compared to Shakespeare’s English is to our modern-day speech.
Extended notes:
While on this Biblical text comparison, it should be noted, that just like the Bible, all the original texts of the Daodejing were lost or destroyed long ago. Just as with the scripture used to create the Bible, various manuscripts exist, many with variations or copyist errors. Just as the earliest New Testament scripture (incomplete) is from 170 years after Christ, the earliest Daodejing manuscript (incomplete) is from 100-200 years after the death of Laozi.
The reason that the originals were lost probably has a lot to do with the first Qin Emperor. Upon taking power and unifying China, he ordered the burning and destruction of all books (scrolls/rolls) except those pertaining to Chinese medicine and a few other subjects. The surviving Daodejing manuscripts were either hidden on purpose or simply forgotten about. Some were not unearthed until as late as 1993.
We compared a lot of research by various archeologists and historians before deciding on this as the most accurate and correct version. But one must allow that it may not be perfect, or the actual and original as from the hand of Laozi himself.
Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Excerpt
Excerpt from Chapter 67
一曰慈二曰儉三曰不敢為天下先 is an excerpt from the 67th Chapter of Lao Tzu's (Lao Zi's) Te-Tao Ching (Dao De Jing).
This is the part where the three treasures are discussed. In English, we'd say these three treasures are compassion, frugality, and humility. Some may translate these as love, moderation, and lack of arrogance. I have also seen them translated as benevolence, modesty, and “Not presuming to be at the forefront in the world.” You can mix them up the way you want, as translation is not really a science but rather an art.
I should also explain that the first two treasures are single-character ideas, yet the third treasure was written out in six characters (there are also some auxiliary characters to number the treasures).
If Lao Tzu's words are important to you, then a wall scroll with this passage might make a great addition to your home.
Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Chapter 9
This text is the ninth chapter of the Daodejing / Tao Te Ching.
The text reads:
持而盈之、不如其已。揣而梲之、不可長保。 金玉滿堂、莫之能守。 富貴而驕、自遺其咎。 功遂身退、天之道。
This classical Chinese passage comes from the Mawangdui (馬王堆帛書) text.
To hold until full is not as good as stopping.
An oversharpened sword cannot last long.
A room filled with gold and jewels cannot be protected.
Boasting of wealth and virtue brings your demise.
After finishing the work, withdraw.
持而盈之不如其已揣而梲之不可長保金玉滿堂莫之能守富貴而驕自遺其咎功遂身退天之道 is the Way of Heaven.
Dr. Muller's translation of all 81 Daodejing chapters
Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Chapter 54
This is the Mawangdui version of Daodejing chapter 54.
By its virtue alone can one generation after another carry on the ancestral sacrifice.
Apply it to yourself, and by its power, you will be freed from dross.
Apply it to your household, and your household shall thereby have abundance.
Apply it to the village, and the village will be made secure.
Apply it to the kingdom, and the kingdom shall thereby be made to flourish.
Apply it to an empire, and the empire shall thereby be extended.
Therefore just as through oneself, one may contemplate Oneself;
So through the household one may contemplate the Household;
And through the village, one may contemplate the Village;
And through the kingdom, one may contemplate the Kingdom;
And through the empire, one may contemplate the Empire.
How do I know that the empire is so? By this.
What is firmly rooted cannot be pulled out;
What is tightly held in the arms will not slip loose;
Through this, the offering of sacrifice by descendants will never come to an end.
Cultivate it in your person, and its virtue will be genuine;
Cultivate it in the family, and its virtue will be more than sufficient;
Cultivate it in the hamlet, and its virtue will endure;
Cultivate it in the state, and its virtue will abound;
Cultivate it in the empire, and its virtue will be pervasive.
Hence look at the person through the person;
Look at the family through the family;
Look at the hamlet through the hamlet;
Look at the state through the state;
Look at the empire through the empire.
How do I know that the empire is like that?
By means of this.
Dark Sister
黑闇女 is a Buddhist title that means “dark sister,” “dark one,” or “dark woman.”
There are two sisters:
One is the deva, 功德女 (“merit” or “achieving”), who causes people to acquire wealth.
The other is the “dark one,” 黑闇女, which causes people to spend and waste.
These sisters always accompany each other.
Double Happiness Guest Book
Customize a special Asian guest book for your wedding
Start customizing a “Double Happiness Guest Book Wall Scroll” Here!
The paper panel length can be whatever you choose from 68cm to 135cm (27” to 53”).
If you don't mention what paper length you want in the special instructions tab (on the next page), we'll make it about 100cm (40”).

The medium-size scroll with a 33cm x 100cm (13” x 40”) paper panel can usually handle up to 89 signatures. That breaks down to 37 signatures per empty square and 15 signatures around the 囍 character. If you switch to a 135cm paper panel, add another 37 potential signatures.
We can splice two 135cm papers together, but that would be a crazy-long scroll. These are only estimates, your mileage may vary.
With silk panels, this will yield a wall scroll about 155cm (61”) long. That's enough for up to 89 signatures. Of course, that depends on if your guests just sign a brief salutation and name, or more verbose good wishes. Customer feedback is that 126 people can sign the 135cm long paper on a medium-sized scroll. If we go bigger than that, there will be a minor paper seam and an extra charge. Email me with your specifications if you need something special.
Most customers pick the festive red paper with gold flecks and white or ivory silk. Red is a good luck color in Chinese culture, thus the most popular choice. But, you can do any color combination that you want.
There is a long history of Chinese-character-use outside of mainland China. This Double Happiness character is also seen at weddings in Korea, Vietnam, Hong Kong, and Taiwan, as well as in Chinese communities in Thailand, Indonesia, and elsewhere. While Japan borrowed Chinese characters into their language, you won't see 囍 as often at Japanese weddings.
The farts of others stink, but one’s own smells sweet
A Bright Future
Incredible 10,000-Mile Flight of the Peng
鵬程萬里 is an ancient Chinese proverb used in modern times to wish someone a long and successful career.
It's really about the 10,000 Flight of the Peng (Peng, also known as Roc is a mythical fish that can turn into a bird and take flight).

莊子
Zhuangzi or Chuang Tzu
Breaking down each character:
1. Peng or Roc (a kind of bird).
2. Journey (in this case, a flight).
3. 10,000 (Ten Thousand).
4. Li is a unit of distance often referred to as a “Chinese Mile,” though the real distance is about half a kilometer.
Direct Translation: “Peng's Journey [of] 10,000 Li.”
Literal meaning: “The 10,000-Li Flying Range Of The Roc.”
Perceived meaning: “To have a bright future” or “To go far.”
This proverb/idiom comes from the book of Zhuangzi or Chuang Tzu. It tells the tale of a huge fish that could turn into a gigantic bird. This bird was called a “peng” and was many miles long. This legendary size allowed the Peng to fly from the Northern Sea to the Southern Sea in a single bound.
Wishing someone “a Peng's Journey of 10,000 Li” will imply that they can travel far without stopping and will have great success, a long career, and a prosperous future.
Flourish
Rise and Fall / Ups and Downs
Eiko-Seisui
This Japanese proverb can be translated as “flourish and wither, prosper and perish,” “life is full of fortune and misfortune,” or simply “vicissitudes of life.”
栄枯盛衰 / 榮枯盛衰 is about the rise and fall of human affairs or the ups and downs of life. Prosperity comes and goes, everything is fleeting and temporary, but like waves, another swell of prosperity may come.
Here's how the Kanji break down in this proverb:
栄 = prosper; thrive; flourish; boom.
枯 = wither; die.
盛 = prosperous; flourishing; thriving; successful; energetic; vigorous; enthusiastic.
衰 = become weaker; decline; get weak; die down; subside; abate; fail.
![]() Notes: The original version of the first character looks like the image to the right. In modern Japan, they simplified that Kanji a bit into the version shown above. If you have a preference for which style is used for your calligraphy, please let me know when you place your order.
Notes: The original version of the first character looks like the image to the right. In modern Japan, they simplified that Kanji a bit into the version shown above. If you have a preference for which style is used for your calligraphy, please let me know when you place your order.
Apparently, with that original version of the first character, this is also used in Korean Hanja. However, I have not confirmed that
it’s
used in the same way or is widely-known in Korean.
Good Luck / Good Fortune
福 is pronounced “fu” in Chinese.
The character “fu” is posted by virtually all Chinese people on the doors of their homes during the Spring Festival (closely associated with the Chinese New Year).
One tradition from the Zhou Dynasty (beginning in 256 B.C.) holds that putting a fu symbol on your front door will keep the goddess of poverty away.
福 literally means good fortune, prosperity, blessed, blessedness, happiness, and fulfillment.
You'll also see this character in Vietnam (where Chinese characters were the written form until a romanization reform) where it is pronounced Phúc - a word commonly used in Vietnamese names because of its good meaning.
See Also: Lucky
Fu Lu Shou
These are the short titles for Sanxing or 三星 (Three Stars).
福祿壽 are the gods of Jupiter, Ursa Major, and Sirius. Fu, Lu, and Shou represent fortune (福), presiding over the planet Jupiter, prosperity (祿), presiding over Ursa Major, and longevity (壽), presiding over Sirius.
In old Chinese folk religion, they are often represented as three old bearded wise men.
Lucky Star
Good Health / Healthy / Vigor
Also suggests being at peace
康 is a single character that means good health or vigor in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
康 can also mean peaceful, at ease, or abundant in some contexts.
Please note that this is rarely seen alone in Japanese Kanji. In Japanese, it is used both for health-related compound words and to denote the kouhou through koushou eras of Japan.
In Korean, this can also be the family name “Kang” (caution: not the only family name romanized as Kang in Korean).
Protect Guard Treasure Cherish
Guanxi
The Chinese Concept of Relationship and Exchange of Favors
The dictionary definition is:
Relations/relationship, to concern, to affect, to have to do with, or connection.
But there's more to it...
In China, the relationship that you have with certain people can open doors for you. Having guanxi with someone also means they would never defraud you but are honor-bound to treat you fairly (of course, this goes both ways). Sometimes it is suggested that guanxi is the exchange of favors. 關繫 / 関繫 / 關係 is more about having a relationship that allows you to ask for and expect favors without shame.
There is no concept in western culture that exactly matches guanxi, but perhaps having a social or professional network is similar.
Note that there are some variations common within Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and Korean Hanja for this word... Japanese tend to use a Chinese alternate form as shown to the right for
Japanese tend to use a Chinese alternate form as shown to the right for
the first character.
 There's also another alternate form of that first character (currently used as the official Simplified form in mainland China) which looks like the character shown to the right. It's basically the central radical of the alternate version shown above but without the “door radical” around it. In more free-flowing calligraphy styles, this version would be the likely choice for a calligrapher.
There's also another alternate form of that first character (currently used as the official Simplified form in mainland China) which looks like the character shown to the right. It's basically the central radical of the alternate version shown above but without the “door radical” around it. In more free-flowing calligraphy styles, this version would be the likely choice for a calligrapher.
![]() In Modern Japanese, they use the character shown to the right.
In Modern Japanese, they use the character shown to the right.
They also tend to use this same form in Korean Hanja (I've only checked this word in my Korean dictionary, but it has not been confirmed by a translator's review).
![]() If that was not confusing enough, there is another alternate form of that second character. See right.
If that was not confusing enough, there is another alternate form of that second character. See right.
An Asian calligrapher of any nationality may use these forms at their discretion. However, They would tend to stick to the most common form used in their respective languages.
If you have any preference on any of these issues, please give us a special note with your order, and we'll make sure it's done the way you want.
Gung Ho
Working Together
工合 is one of those Asian words that is used more in English than in the original Chinese.
Gung Ho was originally used to speak of Carlson's Raiders, a group of “Gung Ho” U.S. Marines who went on an island-hopping campaign of death during WWII.
A movie called Gung Ho came out in the mid-1940s and was later re-released in the 1950s depicting the 2nd Marine Raider Battalion, and brought this word to the mainstream.
It is still sometimes used today within the U.S. Marine Corps brotherhood to refer to a unit or group that works well together or is otherwise efficient and motivated (has good morals).
In 1986, there was a movie called Gung Ho about a Japanese company taking over an American automotive factory. They completely ignored the fact that this was a Chinese title.
It should be noted that this title actually means a condition, state, manner, or the health of something in Japanese.
Language and pronunciation notes:
Like many Asian words absorbed into common use in English, this one is drastically mispronounced. The official Romanization is “gong he” but that doesn't tell you enough. The vowel sound on the first character is like the English word “own,” now just add the g-sounds to the beginning and end. The second character is misleading, as you might think it is like the English word “he.” In reality, the vowel sound is more like the “u” in “up.”
It should also be noted that the current generation in China no longer uses or recognizes this as a common word or slogan.
Note: This can be pronounced and is a word in Japanese, though seldom used. Japanese will use a variation of "具合" instead. But still, not common.
Happiness / Contentment
滿足 is the kind of happiness that involves being satisfied and content.
This can also suggest the actions of “to satisfy,” and “to meet the needs of.”
Other single-word definitions include satisfaction, contentment, sufficient, enough, adequate, full, or complete.
![]() In Japanese, the Kanji for this word is an alternate Chinese form. You can see and select this version at the right (recommended only if your audience is specifically Japanese).
In Japanese, the Kanji for this word is an alternate Chinese form. You can see and select this version at the right (recommended only if your audience is specifically Japanese).
See Also: Satisfaction | Contentment | Pleasure | Well-Being
Glory and Honor
榮 relates to giving someone a tribute or praise.
It's a little odd as a gift, so this may not be the best selection for a wall scroll.
I've made this entry because this character is often misused as “honorable” or “keeping your honor.” It's not quite the same meaning, as this usually refers to a tribute or giving an honor to someone.
榮 is often found in tattoo books incorrectly listed as the western idea of personal honor or being honorable. Check with us before you get a tattoo that does not match the meaning you are really looking for. As a tattoo, this suggests that you either have a lot of pride in yourself or that you have a wish for prosperity for yourself and/or your family.
![]() In modern Japanese Kanji, glory and honor look like the image to the right.
In modern Japanese Kanji, glory and honor look like the image to the right.
There is a lot of confusion about this character, so here are some alternate translations for this character: prosperous, flourishing, blooming (like a flower), glorious beauty, proud, praise, rich, or it can be the family name “Rong.” The context in which the character is used can change the meaning between these various ideas.
In the old days, this could be an honor paid to someone by the Emperor (basically a designation by the Emperor that a person has high standing).
To sum it up: 榮 has a positive meaning; however, it's a different flavor than the idea of being honorable and having integrity.
Hua Mulan
花木蘭 is the name of the famous Chinese woman warrior Hua Mulan.
She was made famous in the west by Disney's animated movie, “Mulan.”
Most of the historical information about her comes from an ancient poem. It starts with a concerned Mulan, as she is told a man from each family is to serve conscription in the army. Her father is too old, and her brother is too young. Mulan decides to take the place of her father. After twelve years of war, the army returns, and the best warriors are awarded great posts in the government and riches. Mulan turns down all offers and asks only for a good horse for the long trip home. When Mulan greets visiting comrades wearing her old clothes, they are shocked to find the warrior they rode into battle with for years is actually a woman.
I am Enough
Three Treasures of Chinese Medicine
精, 氣, 神 are the characters jing, qi, and shen.
As a set, these three characters are known in English as the treasures of traditional Chinese medicine, the treasures of Qi Gong, or the three treasures of Taoism / Daoism.
Sometimes this set is titled 三寶 (sānbǎo) or “three treasures,” but here, we're writing each treasure out.
Here's how these characters are perceived in this context...
Jing: nutritive essence; refined; perfected; pure
Qi: vitality; energy; force; breath; vigor
Shen: spirit; soul; mind; being
To keep it simple, you can use “essence, vitality, and spirit” to define these.
Mutual Welfare and Benefit
Jita-Kyoei
自他共栄 can be translated in a few different ways. Here are some possibilities:
Benefit mutually and prosper together.
Mutual welfare and benefit.
A learning concept of mutual benefit and welfare (that applies to all fields of society).
Mutual prosperity.
The first two characters are easy to explain. They are “self” and “others.” Together, these two characters create a word that means “mutual” (literally “me and them”).
The third character can have different meanings depending on context. Here, it means “in common” or “to share.”
The fourth character suggests the idea of “prosperity,” “flourishing,” or becoming “glorious.”
It should be noted that these Kanji are used almost exclusively in the context of Judo martial arts. 自他共榮 is not a common or recognized Japanese proverb outside of Judo.
You may see this romanized as Jita-Kyoei or Jitakyoei.
In modern Japanese Kanji, the last character looks like ![]() instead of
instead of ![]() . If you want the older/traditional version, please let us know when you place your order.
. If you want the older/traditional version, please let us know when you place your order.
Safety and Well-Being of the Family
Kanai Anzen
家內安全 is the Japanese way of saying “Family First.”
It's a Japanese proverb about the safety and well-being of your family and/or peace and prosperity in the household.
Some Japanese will hang an amulet in their home with these Kanji. The purpose is to keep your family safe from harm.
According to Shinto followers, hanging this in your home is seen as an invocation to God to always keep family members free from harm.
We were looking for a way to say “family first” in Japanese when this proverb came up in the conversation and research. While it doesn't say “family first,” it shows that the safety and well-being of your family is your first or most important priority. So, this proverb is the most natural way to express the idea that you put your family first.
See Also: Peace and Prosperity
Kindness and Forgiving Nature
仁恕 is a word in Chinese and Japanese that means something like benevolence with magnanimity or kindness with a forgiving nature.
If this describes you, then you are the type of person that I would like to call my friend.
This may not be the most common word in daily use, but it's old enough that it transcended cultures from China to Japan in the 5th century when Japan lacked a written language and absorbed Chinese characters and words into their language.
Note: 仁恕 is not commonly used in Korean.
Contentment
知足 means content with one's situation or to know contentment (hence happiness).
From the Zen Buddhist context, Chisoku or 知足 (knowing what’s enough) means always to know and be
satisfied with one’s lot.
Human pain and suffering are born of greed, and that greed arises because we do not know what’s enough.
The Chinese philosopher, Menzi (372-289 BCE) said, “to nourish the mind, there is nothing better than to make the desires few.”
This relays the idea that the best method to cultivate the mind is to have little desire.
Kowtow - The deepest bow
叩頭 is the term that seems to be known worldwide as kowtow.
In Japanese and Chinese, it simply means a deep bow, especially one so low that one's head touches the ground in submission. However, in western culture, it has sometimes come to mean “giving in” or “surrendering to someone else's will.” Sometimes even said of a person who stoops to flattery at the expense of their dignity.
I don't know if you would really want this on a wall scroll, but enough people have searched for this term on our website that I guess it was time to add it. It just feels strange to see such a word on a wall scroll, so please order with caution. 叩頭 is antiquated in both Japanese and Chinese. The act is seldom done anymore and is seen as an ancient ritual.
Live Together and Help Each Other
Large River
江 means large river in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja. This generally refers to a river big enough that it's navigable by cargo boats, passenger boats, or small ships.
In Japanese, this can be a surname when pronounced as Minkou or just Kou.
Learn from Wisdom
(When you see a wise person, try to be like them)
When you meet a wise person, you should learn from them and be inspired to become as wise as they are.
見賢思齊 is a pretty long proverb in English, but in Chinese, it's only four characters.
However, in Chinese, the deeper meaning often surpasses the dictionary definition of each character.
In this case, you should seek wise people to learn from throughout your life...
Always try to learn enough to become equal to them. It also suggests that learning and seeking wisdom is a non-ending cycle.
See Also: Knowledge
A Life of Happiness and Prosperity
幸福成功的一生 means “A life of happiness and prosperity” or “A life of happiness and success.”
It's a very positive and inspirational wall scroll selection.
See Also: Prosperity
A Life of Happiness and Prosperity
幸福と繁栄の人生 is a Japanese proverb that means “A life of happiness and prosperity” or “A life of happiness and success.”
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
See Also: Prosperity
Lioness
雌獅 is how to write “lioness” in Chinese.
Note: 雌獅 is not a very common title for a wall scroll in China. Perhaps because lions are not indigenous to China. Though oddly enough, the rarity of lions made them very prized - and lion dances are a popular festival attraction.
If you see the name of this animal species written on a wall scroll, it's more likely to be the masculine form of “lion.”
Just as Liquor Turns a Face Red, Gold Turns a Heart Black
白酒紅人面黃金黑世心 literally says: [Just as] white liquor makes people's faces turn red, [So] yellow gold makes people's hearts turn black.
This is a warning about the nature of greed. The suggestion is that one who lusts for gold and riches will eventually have a black heart (or become a heartless greedy bastard). As a wall scroll, this is a reminder and warning to keep yourself from following the greedy path.
Live for What You Love
人生謳歌 means “live for what you love” in Japanese.
The first two characters mean “human life” or simply “living.” The last two characters mean “merit,” “prosperity,” or “what you enjoy.” This phrase can suggest working or staying busy for your own goals (in your career).
See Also: Prosperity
Live in Prosperity
生活于繁榮中 means “live in prosperity.” It's kind of a suggestion to be prosperity the center of your world.
This is the way some people want to live (and you should always live for what you love). However, this phrase does not suggest a peaceful life - rather one that is always busy. It's not for everyone, but it might be for you.
See Also: Prosperity
Live Free or Die
Give me liberty or give me death
不自由毋寧死 means “Give me liberty or give me death” in Chinese.
This is also the best way to say, “Live free or die.”
The characters break down this way:
不 = Not; none; without.
自由 = Freedom; liberty; freewill; self-determination.
毋寧 = Rather; would rather; rather be.
死 = Dead; death.
This will go nicely next to your “Don't tread on me” flag. This phrase is known well enough in China that it's listed in a few dictionaries. Though I doubt you will find too many Chinese citizens willing to yell this on the steps of the capital in Beijing.
See Also: Death Before Dishonor
Live Long and Prosper
Longevity / Long Life Wishes
A wish for a long and prosperous life
福如東海壽比南山 is a phrase that means “May you have good fortune as great as the eastern oceans, and may your life last as long as the southern mountains.”
In ancient Chinese mythology, the eastern oceans and southern mountains are where God resides (basically it is the same as saying “heaven”). So it's like saying, “May your good fortune and life be as vast as the heavens.”
There is also a longer, 14-character version of this phrase. Also, this can be cut into two scrolls (with half the phrase on each side - great for hanging on either side of a doorway). Just let me know if you'd like a special version (there is an additional cost).
Longevity / Long Life Wishes
南山之壽 is a wish for long life for someone. The first part of this Japanese phrase is “Nan Zan,” which means “south mountain.” This mountain is one of the good wishes, good fortune, and prosperity. The title is often used as a salutation of good wishes.
The third Kanji is just a connector, and the last Kanji means long life or longevity.
I guess you could translate this phrase as “May your life be as long as Nan Zan is tall.”
Love and Protect
Energy Sword Body in Concert
Spirit, Sword & Body as One
气剑体一致 often gets translated as “Mind Sword Body,” or “Spirit, Sword, and Body as One.” But I think these translations don't tell you enough about what this is really saying.
In this context, 気, which is the modern Japanese version of 氣, means spiritual and unseen energy or “life energy.” In some cases, 気 can be translated as spirit, feeling, or nature. If defined as the mind, it's more about the invisible or intangible parts of one's mind (or soul).
剣 is the Japanese version of 劍 meaning sword.
体 is the modern Japanese version of 體 meaning body.
The Kanji 一 means one, and in this case, suggests “all in one.”
The Kanji 到 means to send, deliver, or convey. But together, 一到 suggests all these things in agreement, union cooperation, or in concert.
Note: Arguments exist as to whether this should be romanized as Kikentaiitchi, Kikentaiicchi, or kikentaiichi. Technically, if you drop the last character, you get 気剣体一 and kikentaiichi (ki ken tai ichi), which is also a valid phrase.
Mind Your Own Business
余計なお世話 suggests that you do not give unwanted help or advice to someone.
The Japanese characters break down this way:
余計 (yokei) too much, unnecessary, extraneous, abundance, surplus, excess, superfluity.
な (na) connecting article.
お世話 (osewa) help, aid, assistance.
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Precious
Precious / Treasure
貴重品 means precious or treasured as an adjective or as a noun, valuables or treasures in Japanese.
貴重品 exists in the Korean dictionary but is rarely if ever, used in Korea.
Prosperity
繁榮 means “prosperous,” “flourishing,” or “thriving” when used regarding a person.
However, when used about a whole country, it can mean a “booming economy.”
繁榮 is the traditional Chinese, ancient Japanese Kanji, and ancient Korean Hanja version of prosperity.
![]() Note: If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, the second character may look more like the Kanji shown to the right. If you want a different form, please note that in the special instructions for your order.
Note: If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, the second character may look more like the Kanji shown to the right. If you want a different form, please note that in the special instructions for your order.
Realize Your Ambitions / Ride on the Crest of Success
大展宏圖 is a four-character proverb used in Chinese to mean “realize your ambitions” or “exhibit your ambition and success.”
It's used to talk about someone with great career ambitions. Almost literally, it expresses the idea of someone unfolding a great career like a map or a set of blueprint plans.
Very literally translated, these four characters mean “Great unfolding of a huge map” or “Great exhibition of a colossal plan.”
Prosperity and Happiness
富樂 is the Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja for a title meaning prosperity and happiness.
If you have the desire to live in prosperity and happiness, this is for you.
Note: This title is often used in a Buddhist context.
Prosperity
繁栄 is the same “prosperity” as the Traditional Chinese version, except for a slight change in the way the second character is written (it's the Japanese Kanji deviation from the original/ancient Chinese form).
Chinese people will still be able to read this, though you should consider this to be the Japanese form (better if your audience is Japanese).

Sometimes, the Kanji form shown to the right is used in Japanese. It will depend on the calligrapher's mood as to which form you may receive. If you have a preference, please let us know at the time of your order.
Prosperity
(also means salary)
祿 is occasionally used in China to mean prosperity or good fortune.
祿 once meant the “official's salary” in old feudal China and Korea (obviously, the officials lived well, so you can imagine how this was associated with the idea of being prosperous).
祿 is only used in Korean historical documents for “salary.” In old Japanese, this means fief, allowance, stipend, reward, pension, grant, and sometimes happiness depending on context. It's very obscure in modern Japanese.
We have other entries that are better suited for a prosperity wall scroll. This entry just addresses “the coffee cup issue” where this character has been used on coffee cups and tee-shirts. However, without context, the meaning is ambiguous to some.
Prosperous Business
興隆 is a kind of prosperity that applies to a business. Something great to hang behind your desk if you are a small or large business owner. Doing so says that you either are a booming business or you wish success and prosperity for your business.
Can also be translated as thriving, flourishing, brisk business, and other words related to prosperity in business.
A good meaning in China but is a little antiquated in Japanese.
See Also: Prosperity
Prosperous Life
Red Envelope
紅包 literally means “red treasure.”
Depending on the context, it can also mean “money wrapped in red as a gift,” “a bonus payment,” “a kickback,” or “a bribe.”
However, most of the time, this is an innocent gift of money in a red envelope that is given from an elder relative to a youngster. This usually happens during the Chinese New Year. It can also happen in preparation for or during a wedding in China.
紅包 is pronounced “Hong Bao” (with an “oh” vowel sound on hong) in Mandarin Chinese. Filipino Chinese call it “Ang Pao.” There are a few other variations.
Shili / Shiri / Sri
Siddhartha
悉達多 is the name Siddhartha (as in Siddhartha Gautama), the personal name for Śākyamuni.
This same Buddha is also known as “Shakyamuni Gautama,” “Gotama Buddha,” or “Tathagata.”
Siddhartha Gautama was a spiritual teacher in the northern region of the Indian subcontinent who founded Buddhism. He is generally seen by Buddhists as the Supreme Buddha (Sammāsambuddha) of known human history.
The actual meaning of this name in Chinese is the realization of all aims, or simply being prosperous.
This name is sometimes romanized from the original Sanskrit or Pali as Siddhattha (from Siddhattha Gotama), Siddharth, Siddhārtha, or Sarvāthasiddha.
Siddhārtha or Sarvāthasiddha can also be written as 悉達, 悉多, 悉多頞他, or 悉陀.
Star
星 is how “star” is written in Chinese, Japanese, and old Korean.
Thousands of years ago, when this character was first developed, there was the belief that you could see remnants of stars in everything. In fact, some early Chinese men of science suggested that all living things came from “stardust” or cosmic debris. This could explain why the upper portion of this character means “sun” (a star itself) and the lower portion means “birth” or “life.”
Oddly enough, modern-day scientists suggest that we are all made up of cosmic dust. Seems they were getting it right in China at a time when the western world thought the Earth was flat and the Church was claiming that the sun and all cosmic bodies revolved around the Earth.
Success
This Chinese and Japanese word for “success” is often used to refer to “career success” but is also used for other successes in life.
It matches the western dictionary definition of “The achievement of something desired, planned, or attempted.” And It's also used in this old Chinese proverb: 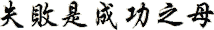 which means Failure is the Mother of Success.
which means Failure is the Mother of Success.
Sometimes this word is translated as prosperity, but success, succeed, or successfully are more correct definitions.
See Also: Prosperity
Sushi
Got a 寿司/sushi restaurant and need an appropriate wall scroll? Or maybe you love sushi enough to have it on your wall. This sushi calligraphy scroll is for you.
Note that the written characters for sushi are the same in Chinese and Japanese. However, the first character is actually a modern Japanese / Simplified Chinese, so in some cases, it will be written differently in Taiwan, Hong Kong, and some older Japanese sushi restaurants where you might see 壽司 instead of 寿司.
Time is more valuable than Jade
Treasure
In Chinese, 珍寶 means treasure, something you value highly, or something very precious to you.
In Japanese, 珍寶 has a meaning like “rare treasure.”
珍 can mean a precious thing or treasure. 寶 can mean a jewel or gem, a treasure, or simply precious. Together these two characters reinforce each other into a word that clearly means treasure.
Treasure
寶 means precious thing or treasure.
This can also mean precious, a gem, a pearl, or anything valuable.
![]() The version of this character shown to the left is the traditional Chinese and ancient/traditional Japanese version. In modern Japan and China, this character has been simplified. This simplified version is shown to the right. If you want this modern Japanese/simplified version, just click the Kanji on the right, instead of the button above. If your audience is Chinese or Korean, I recommend the ancient/traditional form. Only consider the simplified form if your audience is younger Japanese people.
The version of this character shown to the left is the traditional Chinese and ancient/traditional Japanese version. In modern Japan and China, this character has been simplified. This simplified version is shown to the right. If you want this modern Japanese/simplified version, just click the Kanji on the right, instead of the button above. If your audience is Chinese or Korean, I recommend the ancient/traditional form. Only consider the simplified form if your audience is younger Japanese people.
Treasure
財寶 is the Japanese word meaning “treasure” or “money and valuables.”
The first character means “property,” “money,” “wealth,” or “assets.” The second character means “treasure,” “wealth,” or “valuables” in Japanese. Together these two characters reinforce each other into a word that clearly means treasure in Japanese.
財寶 is also a word meaning “money and valuables” in Chinese but more of a daily use word - not as appropriate for a wall scroll if your audience is Chinese.
![]() The second character shown to the left is the ancient/traditional Japanese version. In modern Japan, this character has been simplified. This simplified version is shown to the right. If you want this modern Japanese/simplified version, just click the Kanji on the right, instead of the button above.
The second character shown to the left is the ancient/traditional Japanese version. In modern Japan, this character has been simplified. This simplified version is shown to the right. If you want this modern Japanese/simplified version, just click the Kanji on the right, instead of the button above.
Vinh
Wado-Ryu
Style of Karate or Jujitsu
和道流 or Wado-Ryu is a style of Karate or Jujutsu (Jujitsu).
Note: Many will argue whether this is a style of Karate or Jujutsu.
While some find Wado-Ryu similar to Shotokan Karate, enough differences exist in perspective and technique that it stands by itself.
Breaking down the characters into the proper Japanese Romaji, you have “wa dou ryuu” or “wa dō ryū.” The meaning is roughly-translated as “Harmony Way Style” or “Peace Method Style.” The first Kanji should probably be read as harmony rather than peace in this case.
See Also: Wado-Kai
There is one single thread binding my Way together
吾道一以貫之 is a phrase from the Analects of Confucius that translates as “My Way has one thread that runs through it.”
Other translations include:
My Way is penetrated by a single thread.
There is one single thread binding my Way together.
My Way is run through with a unifying thread.
My Way is Consistent.
And sometimes poetic license is taken, and it is translated as:
My Way is the only one; I'll treasure it and stick to it with humility until the end.
After this was said, some 2500+ years ago, another disciple of Confucius clarified the meaning by stating, “Our master's Way is to be loyal and have a sense of reciprocity.”
In Japanese, this is purported to be romanized as “Waga michi ichi wo motte kore wo tsuranuku,” though some will argue the true pronunciation.
Note: Sometimes written 吾道以一貫之 instead of 吾道一以貫之 with no difference in meaning.
Warrior
The first character, 武, is the spirit or essence of a warrior. The second character, 士, means soldier, officer, or official. 武士 is also used appropriately enough to describe a piece of a chess game. 武士 can also be translated as a soldier, cavalier, palace guard, or samurai, and sometimes as a knight. I've occasionally seen this translated as strong man or tough man (gender not necessarily implied).
By far, 武士 is the most common way to write warrior in Chinese characters, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
Note: In Japanese, this is Bushi, as in Bushido.
Washington
華盛頓 is the name Washington in Chinese.
This can refer to George Washington, Washington State, Washington, D.C., or your surname.
This is old enough that it also means Washington in Japanese (likely a borrowed word from Chinese). Most modern words are written in Katakana in Japanese these days.
Worldwide Wish for Peace and Prosperity
啟盛世開太平 means “To bring flourishing peace and security to the world (our current era).”
It's a wish that a new door leading to peace and prosperity could be opened to mankind.
Character and word breakdown:
啟 to open; to start; to initiate; to enlighten or awaken.
盛世 a flourishing period; period of prosperity; a golden age.
開 to open; to start; to turn on.
太平 peace and security; peace and tranquility; peace; tranquility.
I don't like to do breakdowns like this, as the words altogether create their unique meaning (encompassed in the main title above).
The Whole World at Peace
This proverb can be translated as the whole world at peace, peace and prosperity, peaceful and tranquil, peace reigns over the land, times of peace, peace and tranquillity, peaceful world, or from the Greek, times of halcyon.
Sometimes (rarely) written as 天下泰平 (variant 3rd character).
Boar / Pig
Year of the Pig / Zodiac Sign
豬 is the character for boar, pig, or swine in Chinese and old Korean.
If you were born in the year of the boar/year of the pig, you...
Are optimistic.
Have good luck with wealth and money.
Are honest, generous, and warm-hearted.
![]() The character shown to the right is the Japanese Kanji for "wild boar."
The character shown to the right is the Japanese Kanji for "wild boar."
it’s
an alternate/simplified form of pig/boar in Chinese (can be read by both Chinese and Japanese people). Click on that character instead of the button above if you want this version.
See also our Chinese Zodiac page.
Kanazawa-Ryu
This is the title Kanazawa Ryu in Japanese Kanji.
This can refer to Hirokazu Kanazawa, founder of Shotokan or the city Kanazawa in Japan.
金 = gold
沢 = marsh / swamp / abundance / richness
流 = style / lineage / system / school
So Kanazawa-Ryū literally means:
“Golden Marsh School”
or poetically
“School of Abundant Gold / Rich Spirit.”
The Five Fortunes
Seng
Luong
This in-stock artwork might be what you are looking for, and ships right away...
Unique Good Luck Special Calligraphy Wall Scroll
Discounted Blemished
$17.00 ≈ Kč352.71
The following table may be helpful for those studying Chinese or Japanese...
| Title | Characters | Romaji (Romanized Japanese) | Various forms of Romanized Chinese | |
| Men Die for Wealth, Birds Die for Food | 人為財死鳥為食亡 人为财死鸟为食亡 | rén wèi cái sǐ niǎo wèi shí wáng ren2 wei4 cai2 si3 niao3 wei4 shi2 wang2 ren wei cai si niao wei shi wang | jen wei ts`ai ssu niao wei shih wang jen wei tsai ssu niao wei shih wang |
|
| Money Wealth | 金錢 / 金銭 金钱 | kin sen / kinsen | jīn qián / jin1 qian2 / jin qian / jinqian | chin ch`ien / chinchien / chin chien |
| Wealth Fortune Riches Abundance | 富 | tomi | fù / fu4 / fu | |
| Wealth Riches Fortune | 財富 财富 | cái fù / cai2 fu4 / cai fu / caifu | ts`ai fu / tsaifu / tsai fu | |
| Five Red Bats | 紅五蝠 红五蝠 | hóng wǔ fú hong2 wu3 fu2 hong wu fu hongwufu | hung wu fu hungwufu |
|
| Year-In Year-Out Have Abundance | 年年有餘 年年有馀 | nián nián yǒu yú nian2 nian2 you3 yu2 nian nian you yu niannianyouyu | nien nien yu yü niennienyuyü |
|
| Abundance Prosperous | 富裕 | fu yuu / fuyuu / fu yu | fù yù / fu4 yu4 / fu yu / fuyu | fu yü / fuyü |
| Abundance and Prosperity | 繁榮富裕 繁荣富裕 | hanei yuuhuku haneiyuuhuku hanei yuhuku | fán róng fù yù fan2 rong2 fu4 yu4 fan rong fu yu fanrongfuyu | fan jung fu yü fanjungfuyü |
| Baby | 寶寶 宝宝 | bǎo bao / bao3 bao / bao bao / baobao | pao pao / paopao | |
| The Beatles | ビートルズ | biitoruzu / bitoruzu | ||
| Beautiful Life Life in Perfect Harmony | 和美 | wa mi / wami | hé měi / he2 mei3 / he mei / hemei | ho mei / homei |
| Benzaiten | 弁財天 弁财天 | ben zai ten benzaiten | biàn cái tiān bian4 cai2 tian1 bian cai tian biancaitian | pien ts`ai t`ien pientsaitien pien tsai tien |
| Better to be Happy than Rich | 安貧樂道 安贫乐道 | ān pín lè dào an1 pin2 le4 dao4 an pin le dao anpinledao | an p`in le tao anpinletao an pin le tao |
|
| Blessings on this Home | 五福臨門 五福临门 | wǔ fú lín mén wu3 fu2 lin2 men2 wu fu lin men wufulinmen | ||
| Cherish | 珍愛 珍爱 | zhēn ài / zhen1 ai4 / zhen ai / zhenai | chen ai / chenai | |
| Cherish | 秘蔵 | hi zou / hizou / hi zo | ||
| Daodejing Tao Te Ching - Chapter 33 | 知人者知也自知者明也勝人者有力也自勝者強也知足者富也強行者有志也不失其所者久也死而不亡者壽也 知人者知也自知者明也胜人者有力也自胜者强也知足者富也强行者有志也不失其所者久也死而不亡者寿也 | zhī rén zhě zhī yě zì zhī zhě míng yě shèng rén zhě yǒu lì yě zì shèng zhě qiáng yě zhī zú zhě fù yě qiáng xíng zhě yǒu zhì yě bù zhī qí suǒ zhě jiǔ yě sǐ ér bù wáng zhě shòu yě zhi1 ren2 zhe3 zhi1 ye3 zi4 zhi1 zhe3 ming2 ye3 sheng4 ren2 zhe3 you3 li4 ye3 zi4 sheng4 zhe3 qiang2 ye3 zhi1 zu2 zhe3 fu4 ye3 qiang2 xing2 zhe3 you3 zhi4 ye3 bu4 zhi1 qi2 suo3 zhe3 jiu3 ye3 si3 er2 bu4 wang2 zhe3 shou4 ye3 zhi ren zhe zhi ye zi zhi zhe ming ye sheng ren zhe you li ye zi sheng zhe qiang ye zhi zu zhe fu ye qiang xing zhe you zhi ye bu zhi qi suo zhe jiu ye si er bu wang zhe shou ye | chih jen che chih yeh tzu chih che ming yeh sheng jen che yu li yeh tzu sheng che ch`iang yeh chih tsu che fu yeh ch`iang hsing che yu chih yeh pu chih ch`i so che chiu yeh ssu erh pu wang che shou yeh chih jen che chih yeh tzu chih che ming yeh sheng jen che yu li yeh tzu sheng che chiang yeh chih tsu che fu yeh chiang hsing che yu chih yeh pu chih chi so che chiu yeh ssu erh pu wang che shou yeh |
|
| Daodejing Tao Te Ching - Excerpt | 一曰慈二曰儉三曰不敢為天下先 一曰慈二曰俭三曰不敢为天下先 | yī yuē cí èr yuē jiǎn sān yuē bù gǎn wéi tiān xià xiān yi1 yue1 ci2 er4 yue1 jian3 san1 yue1 bu4 gan3 wei2 tian1 xia4 xian1 yi yue ci er yue jian san yue bu gan wei tian xia xian | i yüeh tz`u erh yüeh chien san yüeh pu kan wei t`ien hsia hsien i yüeh tzu erh yüeh chien san yüeh pu kan wei tien hsia hsien |
|
| Daodejing Tao Te Ching - Chapter 9 | 持而盈之不如其已揣而梲之不可長保金玉滿堂莫之能守富貴而驕自遺其咎功遂身退天之道 持而盈之不如其已揣而梲之不可长保金玉满堂莫之能守富贵而骄自遗其咎功遂身退天之道 | chí ér yíng zhī bù rú qí yǐ chuǎi ér zhī bù kě cháng bǎo jīn yù mǎn táng mò zhī néng shǒu fù guì ér jiāo zì yí qí jiù gōng suì shēn tuì tiān zhī dào chi2 er2 ying2 zhi1 bu4 ru2 qi2 yi3 chuai3 er2 棁 zhi1 bu4 ke3 chang2 bao3 jin1 yu4 man3 tang2 mo4 zhi1 neng2 shou3 fu4 gui4 er2 jiao1 zi4 yi2 qi2 jiu4 gong1 sui4 shen1 tui4 tian1 zhi1 dao4 chi er ying zhi bu ru qi yi chuai er 棁 zhi bu ke chang bao jin yu man tang mo zhi neng shou fu gui er jiao zi yi qi jiu gong sui shen tui tian zhi dao | ch`ih erh ying chih pu ju ch`i i ch`uai erh chih pu k`o ch`ang pao chin yü man t`ang mo chih neng shou fu kuei erh chiao tzu i ch`i chiu kung sui shen t`ui t`ien chih tao chih erh ying chih pu ju chi i chuai erh chih pu ko chang pao chin yü man tang mo chih neng shou fu kuei erh chiao tzu i chi chiu kung sui shen tui tien chih tao |
|
| Daodejing Tao Te Ching - Chapter 54 | 善建者不拔善抱者不脫子孫以祭祀不絕修之身其德乃真修之家其德有余修之鄉其德乃長修之國其德乃夆修之於天下其德乃博以身觀身以家觀家以鄉觀鄉以邦觀邦以天下觀天下吾何以知天下然茲以此 善建者不拔善抱者不脱子孙以祭祀不绝修之身其德乃真修之家其德有余修之乡其德乃长修之国其德乃夆修之于天下其德乃博以身观身以家观家以乡观乡以邦观邦以天下观天下吾何以知天下然兹以此 | shàn jiàn zhě bù bá shàn bào zhě bù tuō zǐ sūn yǐ jì sì bù jué xiū zhī shēn qí dé nǎi zhēn xiū zhī jiā qí dé yǒu yú xiū zhī xiāng qí dé nǎi zhǎng xiū zhī guó qí dé nǎi féng xiū zhī yú tiān xià qí dé nǎi bó yǐ shēn guān shēn yǐ jiā guān jiā yǐ xiāng guān xiāng yǐ bāng guān bāng yǐ tiān xià guān tiān xià wú hé yǐ zhī tiān xià rán zī yǐ cǐ shan4 jian4 zhe3 bu4 ba2 shan4 bao4 zhe3 bu4 tuo1 zi3 sun1 yi3 ji4 si4 bu4 jue2 xiu1 zhi1 shen1 qi2 de2 nai3 zhen1 xiu1 zhi1 jia1 qi2 de2 you3 yu2 xiu1 zhi1 xiang1 qi2 de2 nai3 zhang3 xiu1 zhi1 guo2 qi2 de2 nai3 feng2 xiu1 zhi1 yu2 tian1 xia4 qi2 de2 nai3 bo2 yi3 shen1 guan1 shen1 yi3 jia1 guan1 jia1 yi3 xiang1 guan1 xiang1 yi3 bang1 guan1 bang1 yi3 tian1 xia4 guan1 tian1 xia4 wu2 he2 yi3 zhi1 tian1 xia4 ran2 zi1 yi3 ci3 shan jian zhe bu ba shan bao zhe bu tuo zi sun yi ji si bu jue xiu zhi shen qi de nai zhen xiu zhi jia qi de you yu xiu zhi xiang qi de nai zhang xiu zhi guo qi de nai feng xiu zhi yu tian xia qi de nai bo yi shen guan shen yi jia guan jia yi xiang guan xiang yi bang guan bang yi tian xia guan tian xia wu he yi zhi tian xia ran zi yi ci | shan chien che pu pa shan pao che pu t`o tzu sun i chi ssu pu chüeh hsiu chih shen ch`i te nai chen hsiu chih chia ch`i te yu yü hsiu chih hsiang ch`i te nai chang hsiu chih kuo ch`i te nai feng hsiu chih yü t`ien hsia ch`i te nai po i shen kuan shen i chia kuan chia i hsiang kuan hsiang i pang kuan pang i t`ien hsia kuan t`ien hsia wu ho i chih t`ien hsia jan tzu i tz`u shan chien che pu pa shan pao che pu to tzu sun i chi ssu pu chüeh hsiu chih shen chi te nai chen hsiu chih chia chi te yu yü hsiu chih hsiang chi te nai chang hsiu chih kuo chi te nai feng hsiu chih yü tien hsia chi te nai po i shen kuan shen i chia kuan chia i hsiang kuan hsiang i pang kuan pang i tien hsia kuan tien hsia wu ho i chih tien hsia jan tzu i tzu |
|
| Dark Sister | 黑闇女 | koku an nyo kokuannyo | hēi àn nǚ hei1 an4 nv3 hei an nv heiannv | hei an nü heiannü |
| Double Happiness Guest Book | 囍 喜喜 | xǐ / xi3 / xi | hsi | |
| The farts of others stink, but one’s own smells sweet | 別人屁臭自家香 别人屁臭自家香 | bié rén pì chòu zì jiā xiāng bie2 ren2 pi4 chou4 zi4 jia1 xiang1 bie ren pi chou zi jia xiang bierenpichouzijiaxiang | pieh jen p`i ch`ou tzu chia hsiang pieh jen pi chou tzu chia hsiang |
|
| A Bright Future | 鵬程萬里 鹏程万里 | péng chéng wàn lǐ peng2 cheng2 wan4 li3 peng cheng wan li pengchengwanli | p`eng ch`eng wan li pengchengwanli peng cheng wan li |
|
| Flourish | 興盛 兴盛 | kou sei / kousei / ko sei | xīng shèng xing1 sheng4 xing sheng xingsheng | hsing sheng hsingsheng |
| Rise and Fall Ups and Downs | 栄枯盛衰 / 榮枯盛衰 荣枯盛衰 | ei ko sei sui eikoseisui | ||
| Good Luck Good Fortune | 福 | fuku | fú / fu2 / fu | |
| Fu Lu Shou | 福祿壽 | fú lù shòu fu2 lu4 shou4 fu lu shou fulushou | ||
| Lucky Star | 福星 | fukusei | fú xīng / fu2 xing1 / fu xing / fuxing | fu hsing / fuhsing |
| Good Health Healthy Vigor | 康 | kou / ko | kāng / kang1 / kang | k`ang / kang |
| Protect Guard Treasure Cherish | 護惜 护惜 | goshaku | hù xí / hu4 xi2 / hu xi / huxi | hu hsi / huhsi |
| Guanxi | 關繫 / 関繫 / 關係 关系 / 関係 | kankei | guān xì / guan1 xi4 / guan xi / guanxi | kuan hsi / kuanhsi |
| Gung Ho | 工合 | guai | gōng hé / gong1 he2 / gong he / gonghe | kung ho / kungho |
| Happiness Contentment | 滿足 / 満足 满足 | man zoku / manzoku | mǎn zú / man3 zu2 / man zu / manzu | man tsu / mantsu |
| Glory and Honor | 榮 荣 / 栄 | ei | róng / rong2 / rong | jung |
| Hua Mulan | 花木蘭 花木兰 | huā mù lán hua1 mu4 lan2 hua mu lan huamulan | ||
| I am Enough | 己足以 | jǐ zú yǐ ji3 zu2 yi3 ji zu yi jizuyi | chi tsu i chitsui |
|
| Three Treasures of Chinese Medicine | 精氣神 精气神 | jīng qì shén jing1 qi4 shen2 jing qi shen jingqishen | ching ch`i shen chingchishen ching chi shen |
|
| Mutual Welfare and Benefit | 自他共榮 自他共荣 / 自他共栄 | ji ta kyou ei jitakyouei ji ta kyo ei | ||
| Safety and Well-Being of the Family | 家內安全 家内安全 | ka nai an zen kanaianzen | ||
| Kindness and Forgiving Nature | 仁恕 | jinjo | rén shù / ren2 shu4 / ren shu / renshu | jen shu / jenshu |
| Contentment | 知足 | chisoku | zhī zú / zhi1 zu2 / zhi zu / zhizu | chih tsu / chihtsu |
| Kowtow - The deepest bow | 叩頭 叩头 | koutou / koto | kòu tóu / kou4 tou2 / kou tou / koutou | k`ou t`ou / koutou / kou tou |
| Live Together and Help Each Other | 共存共栄 | kyou son kyou ei kyousonkyouei kyo son kyo ei | ||
| Large River | 江 | kou / ko | jiāng / jiang1 / jiang | chiang |
| Learn from Wisdom | 見賢思齊 见贤思齐 | jiàn xián sī qí jian4 xian2 si1 qi2 jian xian si qi jianxiansiqi | chien hsien ssu ch`i chienhsienssuchi chien hsien ssu chi |
|
| A Life of Happiness and Prosperity | 幸福成功的一生 | xìng fú chéng gōng de yì shēng xing4 fu2 cheng2 gong1 de yi4 sheng1 xing fu cheng gong de yi sheng xingfuchenggongdeyisheng | hsing fu ch`eng kung te i sheng hsingfuchengkungteisheng hsing fu cheng kung te i sheng |
|
| A Life of Happiness and Prosperity | 幸福と繁栄の人生 | kou fuku to ha nei no jin sei koufukutohaneinojinsei ko fuku to ha nei no jin sei | ||
| Lioness | 雌獅 雌狮 | cí shī / ci2 shi1 / ci shi / cishi | tz`u shih / tzushih / tzu shih | |
| Just as Liquor Turns a Face Red, Gold Turns a Heart Black | 白酒紅人面黃金黑世心 白酒红人面黄金黑世心 | bái jiǔ hóng rén miàn huáng jīn hēi shì xīn bai2 jiu3 hong2 ren2 mian4 huang2 jin1 hei1 shi4 xin1 bai jiu hong ren mian huang jin hei shi xin | pai chiu hung jen mien huang chin hei shih hsin | |
| Live for What You Love | 人生謳歌 | jin sei ou ka jinseiouka jin sei o ka | ||
| Live in Prosperity | 生活于繁榮中 生活于繁荣中 | shēng huó yú fán róng zhōng sheng1 huo2 yu2 fan2 rong2 zhong1 sheng huo yu fan rong zhong shenghuoyufanrongzhong | sheng huo yü fan jung chung shenghuoyüfanjungchung |
|
| Live Free or Die | 不自由毋寧死 不自由毋宁死 | bú zì yóu wú nìng sǐ bu2 zi4 you2 wu2 ning4 si3 bu zi you wu ning si buziyouwuningsi | pu tzu yu wu ning ssu putzuyuwuningssu |
|
| Live Long and Prosper | 健康長壽繁榮昌盛 健康长寿繁荣昌盛 | Jiàn kāng cháng shòu fán róng chāng shèng Jian4 kang1 chang2 shou4 fan2 rong2 chang1 sheng4 Jian kang chang shou fan rong chang sheng | Chien k`ang ch`ang shou fan jung ch`ang sheng Chien kang chang shou fan jung chang sheng |
|
| Longevity Long Life Wishes | 福如東海壽比南山 福如东海寿比南山 | fú rú dōng hǎi shòu bǐ nán shān fu2 ru2 dong1 hai3 shou4 bi3 nan2 shan1 fu ru dong hai shou bi nan shan furudonghaishoubinanshan | fu ju tung hai shou pi nan shan fujutunghaishoupinanshan |
|
| Longevity Long Life Wishes | 南山之壽 南山之寿 | nan zan no jyu nanzannojyu | ||
| Love and Protect | 愛護 爱护 | ai go / aigo | ài hù / ai4 hu4 / ai hu / aihu | |
| Energy Sword Body in Concert | 気剣体一致 / 氣劍體一致 气剑体一致 | ki ken tai icchi kikentaiicchi ki ken tai ichi | ||
| Mind Your Own Business | 余計なお世話 | yokei na osewa yokeinaosewa | ||
| Precious | 貴い | tattoi | ||
| Precious Treasure | 貴重品 | ki chou hin kichouhin ki cho hin | ||
| Prosperity | 繁榮 繁荣 | han ei / hanei | fán róng / fan2 rong2 / fan rong / fanrong | fan jung / fanjung |
| Realize Your Ambitions Ride on the Crest of Success | 大展宏圖 大展宏图 | dà jiǎn hóng tú da4 jian3 hong2 tu2 da jian hong tu dajianhongtu | ta chien hung t`u tachienhungtu ta chien hung tu |
|
| Prosperity and Happiness | 富樂 富乐 | furaku | fù lè / fu4 le4 / fu le / fule | |
| Prosperity | 繁栄 繁荣 | hanei | fán róng / fan2 rong2 / fan rong / fanrong | fan jung / fanjung |
| Prosperity | 祿 禄 | fuchi | lù / lu4 / lu | |
| Prosperous Business | 興隆 兴隆 | kou ryuu / kouryuu / ko ryu | xīng lóng xing1 long2 xing long xinglong | hsing lung hsinglung |
| Prosperous Life | 享福 | xiǎng fú / xiang3 fu2 / xiang fu / xiangfu | hsiang fu / hsiangfu | |
| Red Envelope | 紅包 红包 | hóng bāo / hong2 bao1 / hong bao / hongbao | hung pao / hungpao | |
| Shili Shiri Sri | 室利 | shiri | shì lì / shi4 li4 / shi li / shili | shih li / shihli |
| Siddhartha | 悉達多 悉达多 | shiddatta / shiddaruta | xī dá duō xi1 da2 duo1 xi da duo xidaduo | hsi ta to hsitato |
| Star | 星 | hoshi | xīng / xing1 / xing | hsing |
| Success | 成功 | seikou / seiko | chéng gōng cheng2 gong1 cheng gong chenggong | ch`eng kung chengkung cheng kung |
| Sushi | 壽司 寿司 | su shi / sushi | shòu sī / shou4 si1 / shou si / shousi | shou ssu / shoussu |
| Time is more valuable than Jade | 不貴尺之壁而重寸之陰 不贵尺之壁而重寸之阴 | bù guì chǐ zhī bì ér zhòng cùn zhī yīn bu4 gui4 chi3 zhi1 bi4 er2 zhong4 cun4 zhi1 yin1 bu gui chi zhi bi er zhong cun zhi yin | pu kuei ch`ih chih pi erh chung ts`un chih yin pu kuei chih chih pi erh chung tsun chih yin |
|
| Treasure | 珍寶 珍宝 | chin hou / chinhou / chin ho | zhēn bǎo / zhen1 bao3 / zhen bao / zhenbao | chen pao / chenpao |
| Treasure | 寶 宝 | takara | bǎo / bao3 / bao | pao |
| Treasure | 財寶 财宝 | zaihou / zaiho | cái bǎo / cai2 bao3 / cai bao / caibao | ts`ai pao / tsaipao / tsai pao |
| Vinh | 榮 荣 | rong2 / / | ||
| Wado-Ryu | 和道流 | wa dou ryuu wadouryuu wa do ryu | ||
| There is one single thread binding my Way together | 吾道一以貫之 吾道一以贯之 | ware dou tsurayuki waredoutsurayuki ware do tsurayuki | wú dào yī yǐ guàn zhī wu2 dao4 yi1 yi3 guan4 zhi1 wu dao yi yi guan zhi wudaoyiyiguanzhi | wu tao i i kuan chih wutaoiikuanchih |
| Warrior | 武士 | bu shi / bushi | wǔ shì / wu3 shi4 / wu shi / wushi | wu shih / wushih |
| Washington | 華盛頓 华盛顿 | wa shin ton washinton | huá shèng dùn hua2 sheng4 dun4 hua sheng dun huashengdun | hua sheng tun huashengtun |
| Worldwide Wish for Peace and Prosperity | 啟盛世開太平 启盛世开太平 | qǐ shèng shì kāi tài píng qi3 sheng4 shi4 kai1 tai4 ping2 qi sheng shi kai tai ping qishengshikaitaiping | ch`i sheng shih k`ai t`ai p`ing chishengshihkaitaiping chi sheng shih kai tai ping |
|
| The Whole World at Peace | 天下太平 | tenkataihei tenkataihei | tiān xià tài píng tian1 xia4 tai4 ping2 tian xia tai ping tianxiataiping | t`ien hsia t`ai p`ing tienhsiataiping tien hsia tai ping |
| Boar Pig | 豬 猪 | inoshishi | zhū / zhu1 / zhu | chu |
| Kanazawa-Ryu | 金沢流 | kana zawa ryuu kanazawaryuu kana zawa ryu | ||
| The Five Fortunes | 五福 | wǔ fú / wu3 fu2 / wu fu / wufu | ||
| Seng | 盛 | shèng / sheng4 / sheng | ||
| Luong | 梁 | liáng / liang2 / liang | ||
| In some entries above you will see that characters have different versions above and below a line. In these cases, the characters above the line are Traditional Chinese, while the ones below are Simplified Chinese. | ||||











































































































